Chikungunya’s Long-Term Impact: A Global Health Concern
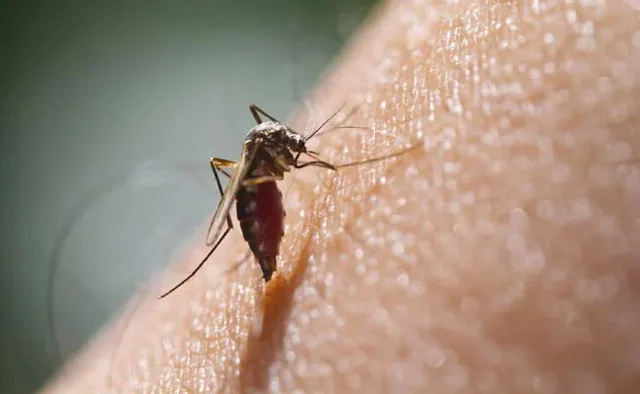
A new global study conducted by the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine highlights the growing concern surrounding chikungunya. While known for causing acute fever, the research emphasizes the long-term disabling effects of this mosquito-borne viral infection.
The Persistent Impact of Chikungunya
Chikungunya’s impact goes beyond the initial fever. The study points to:
- Chronic joint pain that can last for months or even years.
- Debilitating fatigue that affects daily life.
- Potential neurological complications in some cases.
Global Spread and Vulnerable Populations
The chikungunya virus is spread through the bites of infected mosquitoes, primarily *Aedes aegypti* and *Aedes albopictus*. The disease is prevalent in:
- Tropical and subtropical regions.
- Areas with poor sanitation and stagnant water.
- Populations with limited access to healthcare.
Prevention and Management Strategies
Effective prevention and management strategies are crucial to combatting chikungunya:
- Mosquito control measures such as eliminating breeding sites and using repellents.
- Early diagnosis and supportive care to manage symptoms.
- Pain management and physical therapy to address chronic joint pain.
- Further research to develop vaccines and antiviral therapies.
The Need for Increased Awareness and Research
The study underscores the urgent need for increased awareness among healthcare professionals and the public about the long-term consequences of chikungunya. Further research is essential to understand the virus better and develop effective prevention and treatment strategies. Public health initiatives are vital for controlling mosquito populations and educating communities on preventive measures, especially in endemic regions. By addressing these key areas, we can mitigate the impact of chikungunya and improve the quality of life for those affected.

+ There are no comments
Add yours