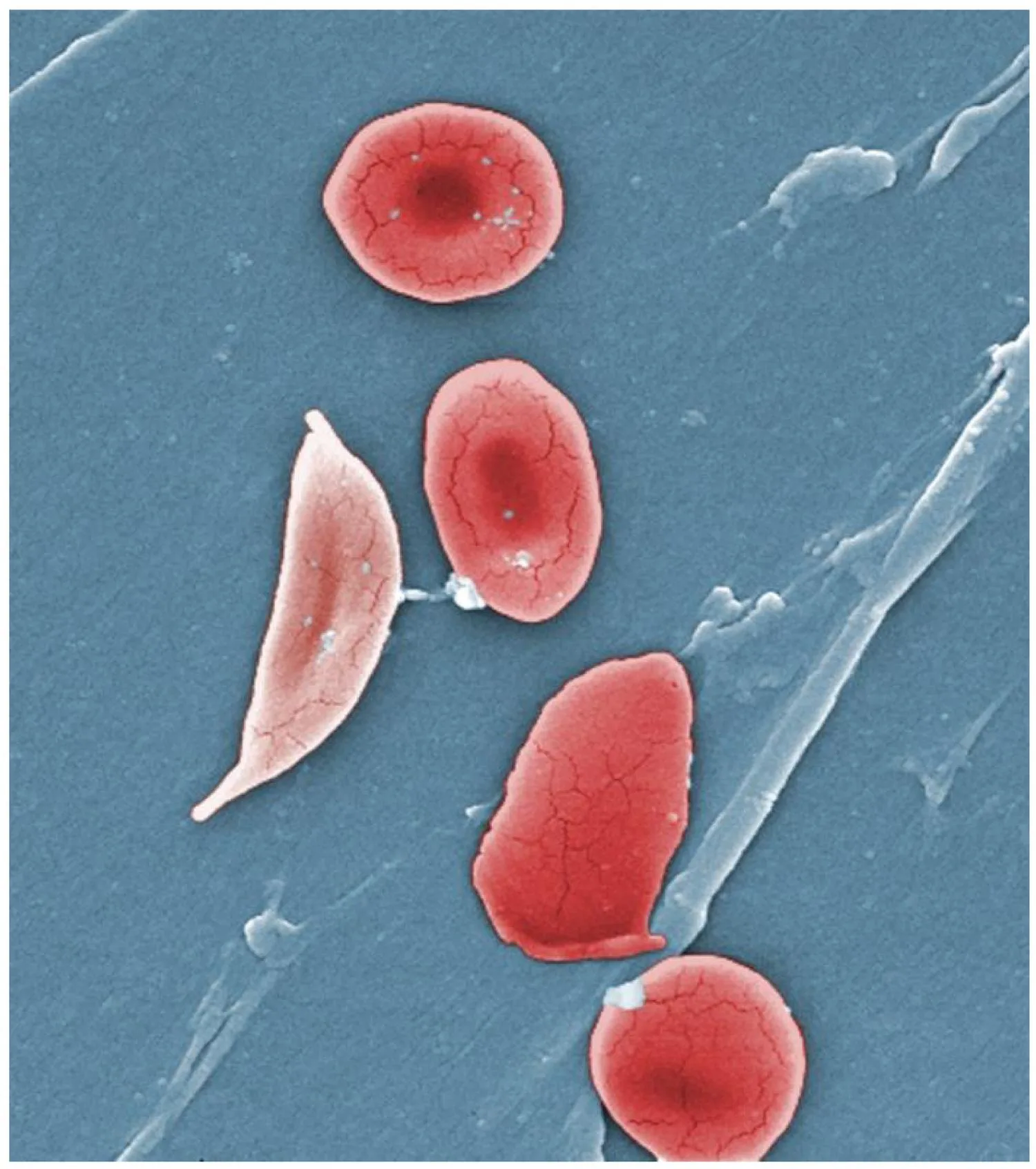
Innovative Program Enhances Life Quality for Teens with Sickle Cell Disease
A groundbreaking study from Columbia University School of Nursing reveals that a new intervention significantly improves the quality of life for adolescents managing sickle cell disease. The program focuses on supporting adherence to hydroxyurea treatment, a crucial aspect of care for these young patients. This research highlights effective strategies for minimizing the impact of this challenging condition.
Understanding the HABIT Efficacy Trial
The study, published in Pediatric Blood & Cancer, details the positive outcomes of the “HABIT Efficacy Trial Intervention.” This intervention specifically targets the unique challenges faced by adolescents with sickle cell disease, aiming to improve their overall well-being and disease-specific quality of life.
Key Components of the Intervention
While the specifics of the intervention are detailed in the full study, the core principle revolves around providing comprehensive support to help adolescents consistently follow their hydroxyurea treatment plans. This likely includes elements such as:
- Education about the importance of hydroxyurea
- Strategies for managing side effects
- Motivational support and counseling
- Family involvement
Why Hydroxyurea Adherence Matters
Hydroxyurea is a vital medication for many individuals with sickle cell disease. Regular use can:
- Reduce the frequency of pain crises
- Decrease the need for blood transfusions
- Improve overall health outcomes
However, adherence can be challenging, especially for adolescents navigating the complexities of managing a chronic illness alongside typical teenage life.
Positive Impact on Quality of Life
The study’s findings demonstrate that the HABIT Efficacy Trial Intervention is successful in improving several aspects of life for adolescents with sickle cell disease. These improvements likely span both general well-being and specific disease-related factors, contributing to a more positive and fulfilling life experience.
Final Words
This research offers a promising avenue for enhancing the lives of young people living with sickle cell disease. By focusing on adherence to hydroxyurea treatment and providing comprehensive support, interventions like the HABIT Efficacy Trial can make a significant difference in their overall health and quality of life. Further research and implementation of similar programs could lead to improved outcomes for countless adolescents affected by this condition.


+ There are no comments
Add yours