Breakthrough Discovery: Targeting cdc42 Could Revolutionize Nephrotic Syndrome Treatment
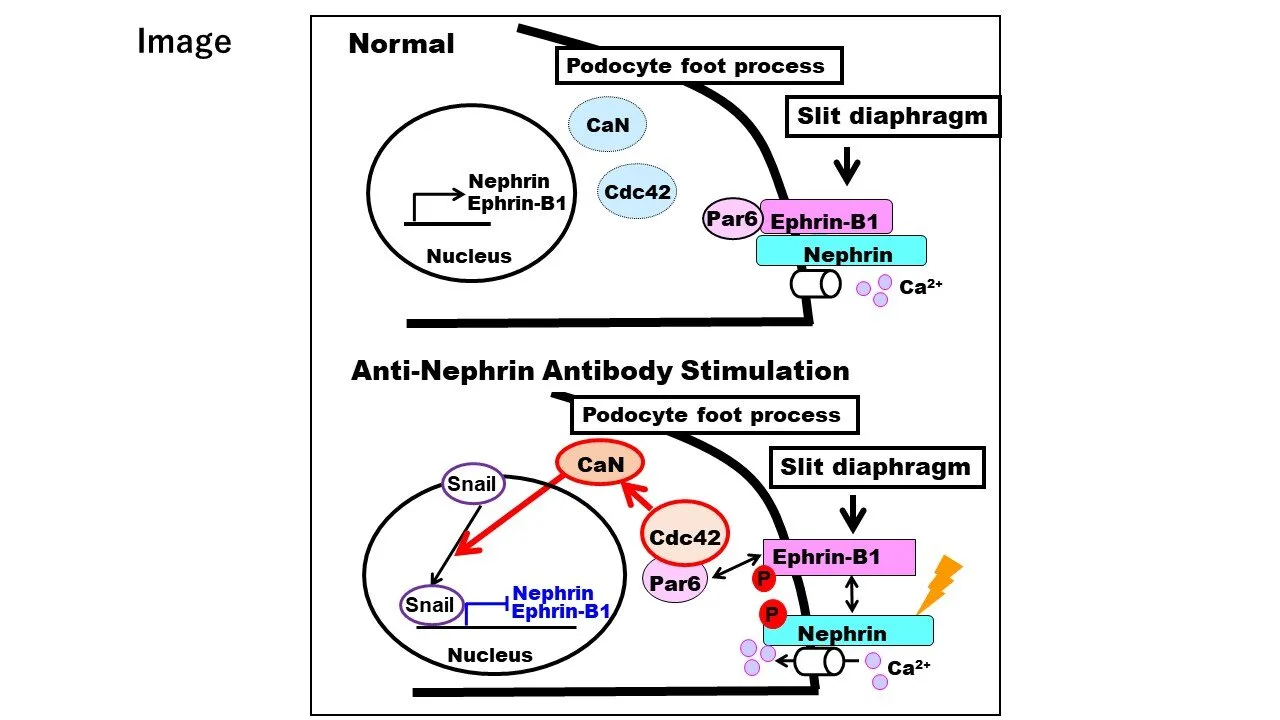
Researchers at Niigata University’s Kidney Research Center have identified a key mechanism behind proteinuria, a hallmark of nephrotic syndrome. The study, spearheaded by the Department of Cell Biology, pinpoints the overactivity of a protein called cdc42 as a critical trigger for the condition. This groundbreaking finding, published in the esteemed Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, opens exciting new avenues for therapeutic intervention.
Understanding Proteinuria and Nephrotic Syndrome
Nephrotic syndrome is a kidney disorder characterized by the leakage of protein into the urine (proteinuria). This protein loss can lead to a range of health problems, including swelling, high cholesterol, and an increased risk of infection. Current treatments often focus on managing symptoms, but this new research offers the potential for a more targeted approach.
The Role of cdc42
The research team discovered that when cdc42 becomes excessively active, it initiates a chain of events that ultimately damage the kidney’s filtering system, leading to proteinuria. This discovery is significant because it identifies a specific target for potential therapies.
A Promising Therapeutic Strategy
Based on their findings, the researchers propose that suppressing cdc42 activity could be a highly effective strategy for treating nephrotic syndrome. This could involve developing drugs that specifically inhibit cdc42 or target the pathways that regulate its activity.
Implications for Future Treatment
This research provides a strong foundation for the development of novel therapies for nephrotic syndrome. By targeting the root cause of the problem – the overactivity of cdc42 – researchers hope to develop more effective and long-lasting treatments for this debilitating condition. Further studies are needed to translate these findings into clinical applications, but the initial results are highly promising.
Key Takeaways:
- Overactive cdc42 is a key initiator of proteinuria.
- Targeting cdc42 could be a new therapeutic avenue for nephrotic syndrome.
- The findings are published in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology.
Final Words
The identification of cdc42’s role in proteinuria marks a significant step forward in our understanding and treatment of nephrotic syndrome. By focusing on this specific molecular target, researchers are paving the way for the development of more effective and targeted therapies that could significantly improve the lives of patients with this condition.

+ There are no comments
Add yours