Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation: A Potential Treatment for Addiction?
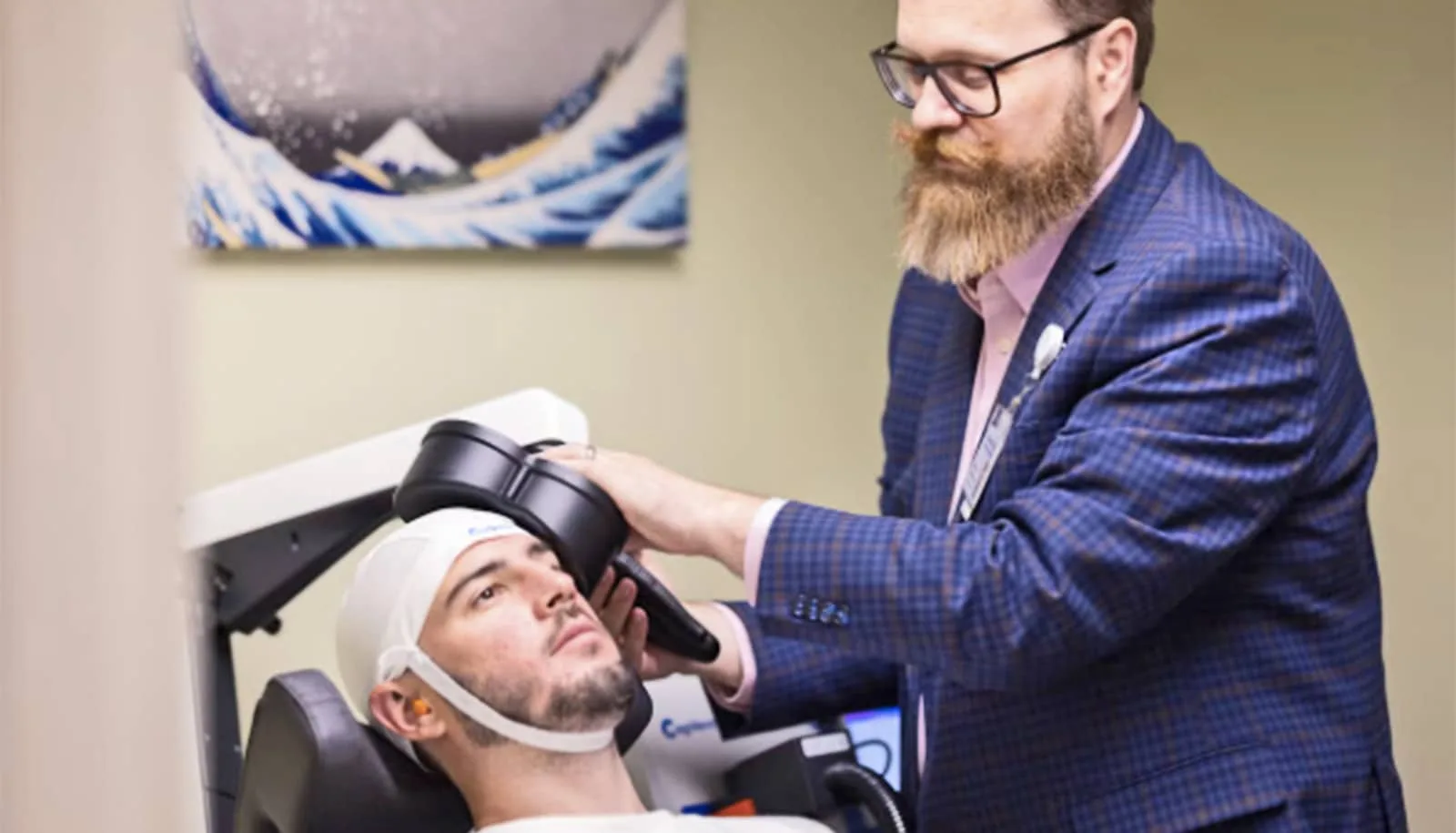
Addiction is a complex and challenging condition affecting millions worldwide. While various treatment options exist, researchers are constantly exploring innovative approaches to combat this pervasive issue. One such promising avenue is transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), a non-invasive technique that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. A scientist is currently conducting research to determine if TMS can be an effective treatment for individuals struggling with addiction.
Understanding Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
TMS involves placing a device on the scalp that delivers magnetic pulses to specific brain regions. These pulses can either stimulate or inhibit neuronal activity, depending on the frequency and intensity of the stimulation. The technique has already been approved for treating depression and is being investigated for other neurological and psychiatric disorders.
How TMS Works for Addiction
The underlying principle behind using TMS for addiction lies in its ability to modulate brain circuits involved in reward, craving, and impulse control. Addiction often disrupts these circuits, leading to compulsive drug-seeking behavior. By targeting specific brain areas with TMS, researchers hope to restore balance and reduce the intensity of cravings.
- Targeting Brain Regions: TMS allows researchers to target specific areas of the brain associated with addiction.
- Modulating Neural Activity: The magnetic pulses can either stimulate or inhibit neural activity, helping to restore balance in disrupted brain circuits.
- Non-Invasive Approach: TMS is a non-invasive technique, making it a potentially safer alternative to other treatments.
The Research Study
The scientist’s research involves carefully designed experiments to assess the effects of TMS on individuals with addiction. Participants undergo a series of TMS sessions, and their cravings, withdrawal symptoms, and substance use patterns are closely monitored. Brain imaging techniques may also be used to examine changes in brain activity following TMS treatment.
Key Aspects of the Study
- Participant Selection: Recruiting individuals with different types of addiction to ensure the findings are generalizable.
- Control Group: Including a control group that receives a sham TMS treatment (placebo) to isolate the specific effects of TMS.
- Outcome Measures: Using a combination of self-report questionnaires, behavioral assessments, and brain imaging to evaluate treatment outcomes.
Potential Benefits and Future Directions
If the research demonstrates that TMS is effective in treating addiction, it could offer a valuable new tool for clinicians and individuals struggling with substance use disorders. TMS has the potential to reduce cravings, prevent relapse, and improve overall quality of life.
Future research could explore:
- Optimizing TMS protocols to maximize treatment efficacy.
- Combining TMS with other therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT).
- Identifying biomarkers that predict who is most likely to benefit from TMS.
Final Words
The investigation into TMS as a treatment for addiction is a promising area of research. While further studies are needed, the early findings suggest that TMS could offer a safe and effective way to help individuals overcome addiction and reclaim their lives. This research highlights the importance of exploring innovative approaches to address the complex challenges of addiction and improve the lives of those affected.


+ There are no comments
Add yours