Brain’s Immune Cells Target Alzheimer’s Culprit
Alzheimer’s disease is a devastating condition affecting millions worldwide. Scientists are continuously working to understand its causes and develop effective treatments. Recent research sheds light on the crucial role of microglia, a type of immune cell residing in the brain, in combating this disease.
Microglia: The Brain’s Clean-Up Crew
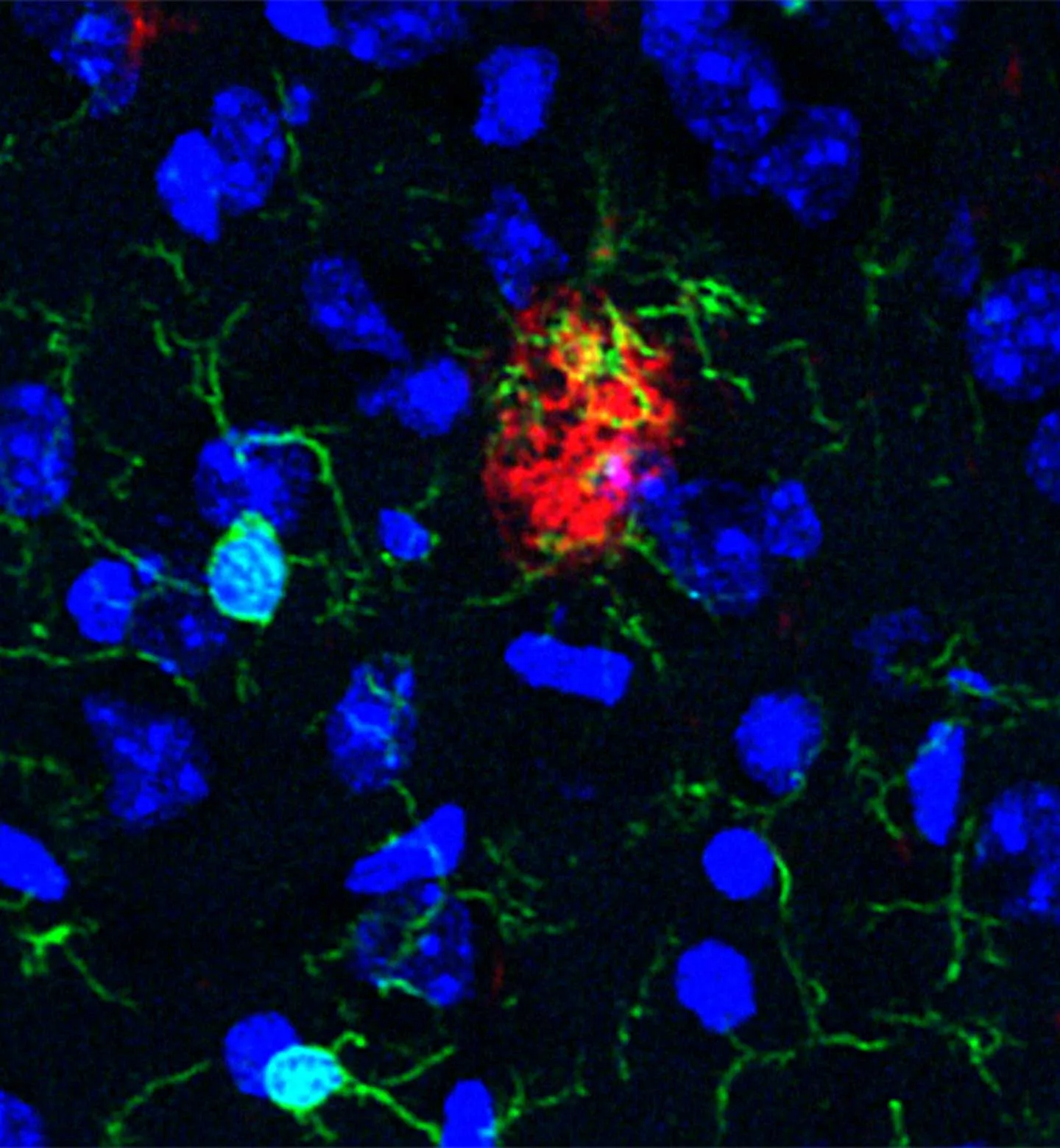
Microglia act as the brain’s resident immune cells, constantly patrolling the neural landscape for threats. One of their key functions is to engulf and remove debris, including harmful substances that can accumulate and impair brain function. In the context of Alzheimer’s disease, microglia have a specific target: amyloid beta.
Amyloid Beta and Alzheimer’s Disease
Amyloid beta is a protein that, under normal circumstances, doesn’t pose a problem. However, in Alzheimer’s disease, amyloid beta misfolds and clumps together, forming toxic aggregates or plaques. These plaques disrupt communication between brain cells and contribute to the cognitive decline characteristic of the disease. Microglia attempt to clear these plaques, acting as a defense mechanism.
How Microglia Combat Amyloid Beta
Microglia possess the ability to phagocytose, or engulf, amyloid beta. They essentially ‘eat’ the protein, breaking it down and removing it from the brain. This process is crucial in slowing the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
The Process:
- Microglia detect amyloid beta plaques.
- They migrate towards the plaques.
- Microglia engulf and internalize the amyloid beta.
- Enzymes within the microglia break down the protein.
Final Words
The role of microglia in combating Alzheimer’s disease is complex and multifaceted. While these immune cells can effectively clear amyloid beta, their function can become impaired as the disease progresses. Further research is needed to understand how to enhance microglial activity and harness their potential to fight Alzheimer’s disease. Understanding microglia’s role offers promising avenues for therapeutic interventions, potentially paving the way for new treatments that can slow or even prevent the progression of this debilitating condition.



+ There are no comments
Add yours