Unlocking Malaria’s Secrets: New Biomarkers for Improved Treatment
Researchers at Northwestern University have made a significant breakthrough in understanding severe malaria infections in children. Their study, recently published in Nature Communications, identifies critical biological markers that could pave the way for more effective treatment strategies.
The Quest for Biomarkers
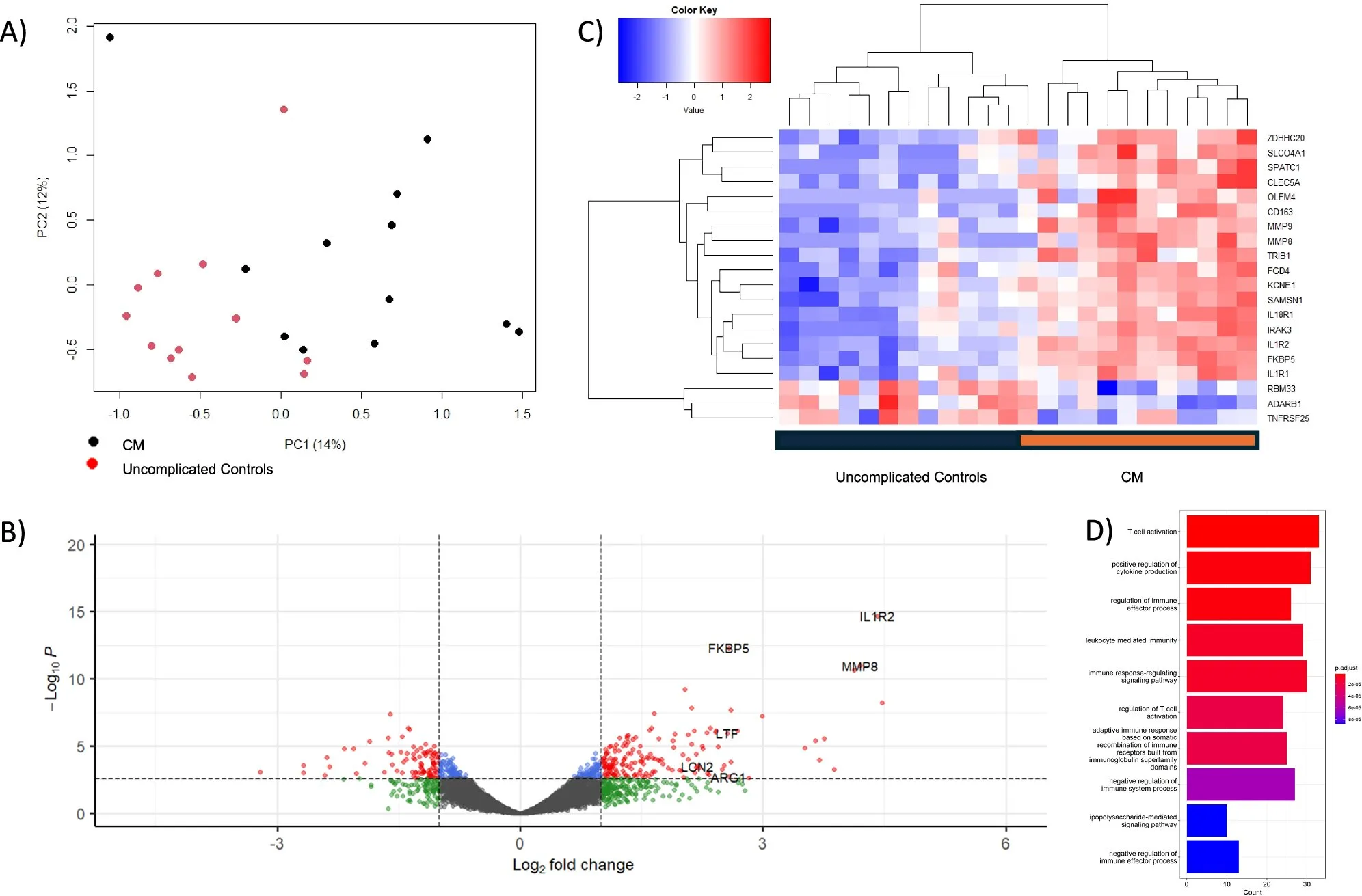
Malaria remains a major global health challenge, particularly for young children in endemic regions. Severe malaria can lead to life-threatening complications, making early diagnosis and targeted treatment crucial. This research focused on identifying specific biomarkers – measurable indicators of a biological state or condition – that could help predict the severity of the disease and guide treatment decisions.
Key Findings
The study pinpointed several biological markers associated with severe malaria in children. These markers provide insights into the complex immune responses and pathological processes that occur during infection. The research suggests that by monitoring these markers, clinicians may be able to:
- Identify children at higher risk of developing severe malaria.
- Tailor treatment approaches based on individual patient profiles.
- Develop new therapies that target specific pathways involved in disease progression.
Implications for Future Treatments
The discovery of these biomarkers represents a significant step forward in the fight against malaria. Further research is needed to validate these findings in larger populations and to translate them into clinical applications. However, the potential impact on improving treatment outcomes for children with severe malaria is substantial.
Final Words
This research offers hope for more effective and personalized approaches to treating severe malaria. By understanding the underlying biological mechanisms of the disease, scientists are paving the way for a future where malaria is no longer a major threat to children’s health.


+ There are no comments
Add yours