Understanding Microglia: The Brain’s Dedicated Defenders
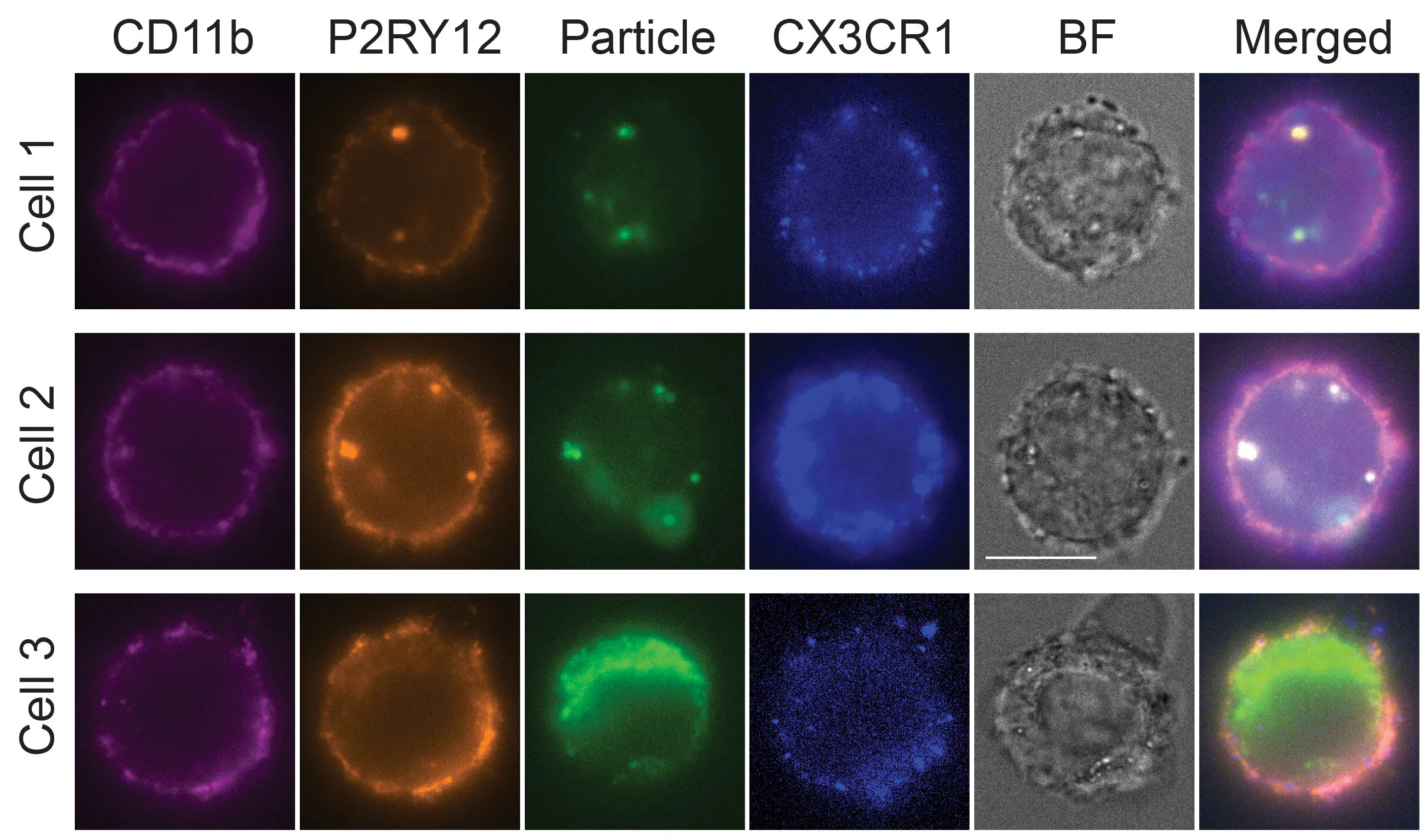
Microglia, a unique form of immune cell, constitute roughly 10% of the cells found within the brain and spinal cord. These specialized cells play a crucial role in maintaining brain health through several key functions.
The Key Functions of Microglia
Microglia act as the brain’s clean-up crew and defense force. Their primary responsibilities include:
- Eliminating Infectious Microbes: They target and remove harmful microorganisms that could cause infections within the brain.
- Removing Dead Cells: Microglia clear away dead or damaged cells, preventing them from causing inflammation or disrupting normal brain function.
- Clearing Aggregated Proteins: They break down and remove clumps of misfolded proteins, which can accumulate and contribute to neurodegenerative diseases.
- Neutralizing Soluble Antigens: Microglia neutralize potentially harmful soluble antigens that may pose a threat to the brain.
Microglia’s Role in Brain Development
Beyond their immune functions, microglia also play a vital role in the developing brain. They help to:
- Shape Neural Circuits: During brain development, microglia assist in sculpting neural circuits, ensuring proper connections and efficient brain function.

+ There are no comments
Add yours