Breakthrough Study Rethinks Penicillin Dosage for Strep A Prevention
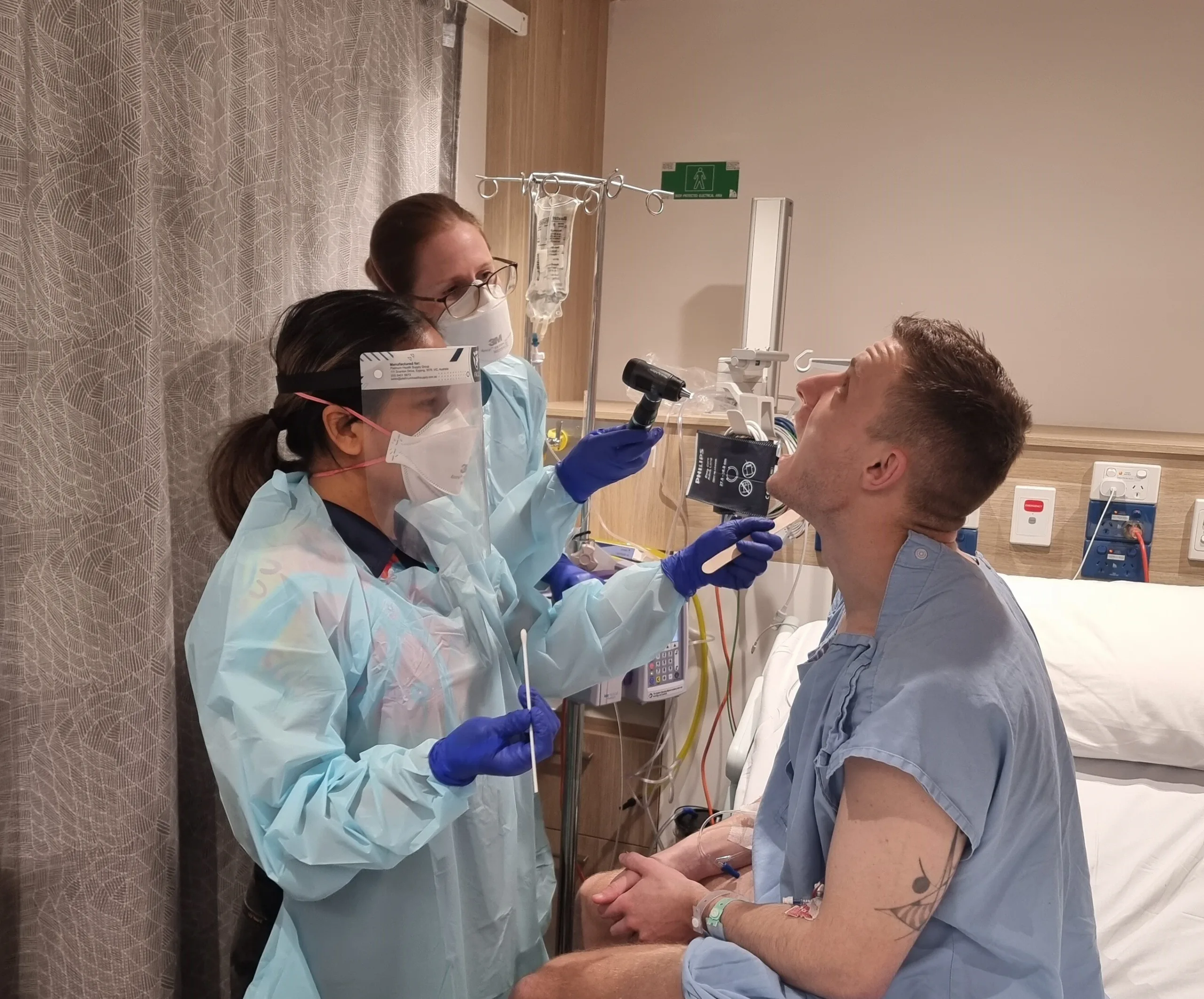
A groundbreaking study involving the deliberate exposure of participants to Streptococcus pyogenes (Strep A) has yielded surprising results. Researchers set out to determine the minimum effective dose of penicillin required to prevent infection. The findings challenge existing assumptions and could revolutionize treatment strategies, particularly for individuals at risk of rheumatic heart disease (RHD).
Key Findings of the Strep A Study
The study’s most significant discovery is that the amount of penicillin needed to ward off Strep A infection is considerably lower than previously believed. This revelation has major implications for how doctors approach preventative care, especially in vulnerable populations.
Implications for Rheumatic Heart Disease (RHD)
Rheumatic heart disease is a serious condition often stemming from untreated Strep A infections. This new understanding of penicillin dosage could lead to more effective and efficient preventative treatments for those living with or at risk of RHD.
- Lower doses may reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance.
- Treatment costs could potentially be lowered, making it more accessible.
- Patients may experience fewer side effects with reduced medication.
Why This Study Matters
This research is a significant step forward in combating Strep A infections and their long-term consequences. By refining our understanding of appropriate penicillin dosages, we can improve patient outcomes and reduce the burden of diseases like RHD.
Future Directions
Further research is needed to explore the optimal penicillin administration protocols based on these findings. This includes investigating the ideal frequency and duration of treatment for different patient groups.
Final Words: A New Era in Strep A Prevention
The results of this innovative study promise a new era in the prevention of Strep A infections. With a clearer understanding of effective penicillin dosages, healthcare professionals can provide more targeted and efficient care, ultimately improving the lives of countless individuals worldwide.

+ There are no comments
Add yours