For years, gout has been primarily associated with diet—particularly the consumption of red meat, seafood, and alcohol. However, recent research has revealed a surprising factor that plays a significant role in the development of this painful condition, reshaping the way we understand and manage it.
The Unexpected Culprit Behind Gout
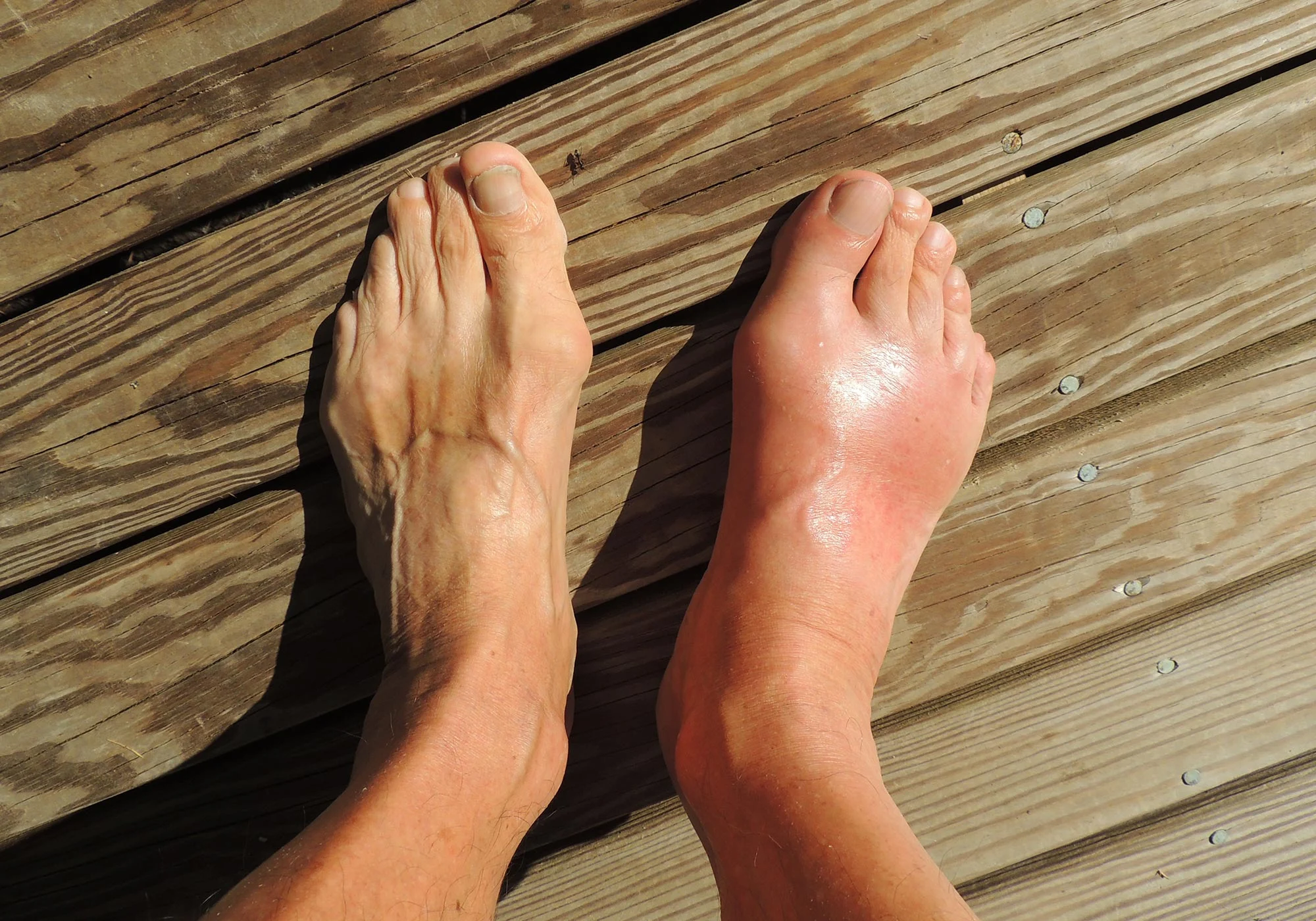
Traditionally, gout has been linked to high levels of uric acid in the blood, which crystallize and cause joint inflammation. While diet influences uric acid levels, new findings suggest that genetics and other metabolic factors may play a more substantial role than previously believed.
Researchers found that certain genetic variations can predispose individuals to inefficient uric acid elimination, increasing the likelihood of developing gout regardless of dietary habits. This discovery indicates that some people may be more susceptible to the condition due to hereditary traits rather than lifestyle choices alone.
Beyond Diet: The Role of Metabolism and Genetics
The study highlights that metabolic issues, including kidney function and insulin resistance, contribute significantly to gout risk. Impaired kidney function reduces the body’s ability to excrete uric acid efficiently, leading to its accumulation in the bloodstream. Additionally, insulin resistance—a common precursor to diabetes—has been linked to higher uric acid levels, further complicating the condition.
What This Means for Gout Prevention and Treatment
With this new understanding, medical professionals may shift their focus from strictly dietary recommendations to a more holistic approach. Genetic testing could help identify at-risk individuals, enabling early intervention through targeted lifestyle modifications and medications that enhance uric acid excretion.
Conclusion
This groundbreaking study challenges long-standing misconceptions about gout. While diet remains an important factor, genetics and metabolic health play a crucial role in the condition’s development. As research continues, personalized treatment plans may offer more effective solutions for managing gout and improving overall health.
#GoutResearch #HealthDiscovery #MetabolicHealth #GeneticsAndHealth #Inflammation #ChronicDisease


+ There are no comments
Add yours